urticaria
What is urticaria?
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by itchy, raised, and red welts or bumps on the skin. These bumps may be small or large, and they can appear anywhere on the body. They may also appear in clusters, and they can vary in shape and size. Urticaria occurs when the body releases histamine and other chemicals in response to an allergen or other trigger. This triggers a response in the skin, causing it to become inflamed and itchy.
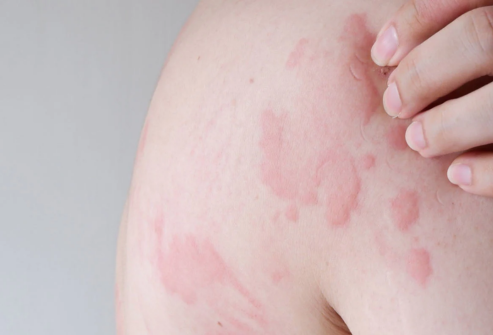
Symptoms
The main symptom of urticaria is the appearance of raised, red, and itchy bumps or welts on the skin, known as hives. These hives can appear suddenly and may disappear quickly, or they may persist for hours or even days. The size and shape of the hives can vary, and they may be clustered together or spread out over a larger area of the body.
- Itching or burning sensation: The hives can be intensely itchy and may cause a burning or stinging sensation.
- Swelling: In some cases, the skin around the hives may become swollen and may feel warm to the touch.
- Pale or red skin: The skin around the hives may appear pale or red, depending on the severity of the reaction.
- Difficulty breathing: In rare cases, urticaria may cause swelling of the throat or other areas of the body, leading to difficulty breathing, wheezing, or other respiratory symptoms.
Causes
Urticaria, also known as hives, can be caused by a variety of factors. Some
common causes of urticaria include:
Allergic reactions: Urticaria can be triggered by an allergic reaction to a specific
substance, such as certain foods, medications, insect bites or stings, or exposure to
environmental allergens like pollen, dust, or animal dander.
Infections: Some infections, such as viral infections or bacterial infections like strep
throat, can trigger an immune response that leads to urticaria.

DR Shruti Bajad
MBBS, MD (Internal Medicine)
Consultant Rheumatologist
